Generalities about fats and lipids: Glycerides
|
Function |
|

|
Fatty acid esters of glycerol are the primary means by which
animals store energy. Fish are able to metabolize lipids readily, particularly
when deprived of food. Dietary lipid has two main functions - as a source of
energy and as a source of its component fatty acids, some of which are
essential (i.e. cannot be synthesised by the animal itself) dietary components
for the growth and survival of the recipient animal. Lipids are also important
factors in the palatability of feeds. The triglycerides are one form of fatty acid esters with
glycerol and make up the majority of dietary and body fat. As already mentioned
they have several roles in the body: energy storage, energy production, satiety
value, insulation, vitamins, essential fatty acids, flavor and texture.
|
Structure |
|

|
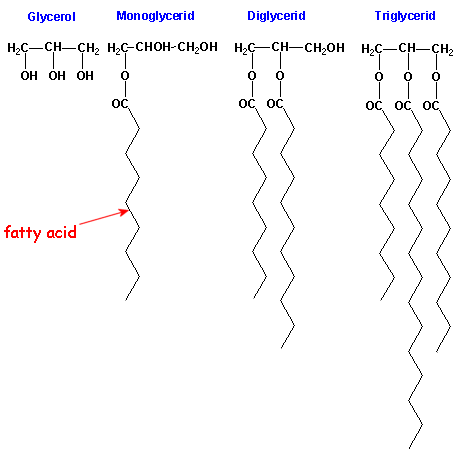 |
| Figure: Schematical drawing of glycerides |
|
3D view |
|

|
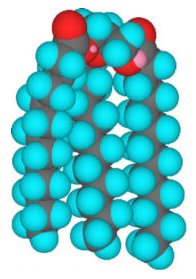 |
| Figure: 3-dimensional view of a triglyceride |
|
Common fatty acids |
|

|
| Common Name |
Systematic Name |
Chemical Abbreviation |
Melting Point (oC) |
Common Source |
| Lauric |
Dodecanoic |
C12:0 |
43.6 |
Coconut |
| Myristic |
Tetradecanoic |
C14:0 |
53.8 |
Coconut and Milk Fat |
| Palmitic |
Hexadecanoic |
C16:0 |
62.9 |
Animal and Vegetable |
| Stearic |
Octadecanoic |
C18:0 |
69.9 |
Animal and Vegetable |
| Arachidic |
Eicosanoic |
C20:0 |
75.2 |
Peanut Oil |
| Palmitoleic |
9-Hexadecenoic |
C16:19 |
-1.5 |
Milk Fat |
| Oleic |
9-Octadecenoic |
C18:1w9 |
14.0 |
Animal and Vegetable |
| Linoleic |
9,12-Octadecenoic |
C18:2w6 |
-11.0 |
Animal and Vegetable |
| Linolenic |
9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic |
C18:3w3 |
-30.0 |
Linseed and Rubberseed |
| Arachidonic |
5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic |
C20:4w6 |
n/a |
Lecithin and Lard |
|
Nomenclature |
|

|
Fatty acids are specified by a numerical designation, such as
14:0; 20:1; 18:3n-3 or 22:6n-3, for example. This nomenclature refers to the
length of the carbon chain in the molecule, the number of carbon-carbon double
bonds present and the position of the first double bond.
| For example: for 20:4n-6 (arachidonic acid), '20' means
that there are 20 carbon atoms in the chain. '4' means that there are four
carbon-carbon double bonds and n-6 means that the first double bond, numbering
from the methyl (CH3) end, occurs after the sixth carbon atom in the chain.
|
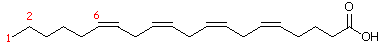 |
| Arachidonic acid |
|
Those fatty acids which have their first double bond on the
third carbon atom are known as the 'n-3' series. Those which have their first
double bond on the sixth carbon atom are known as the 'n-6' series. Saturated
fatty acids are those without any double bonds. Monosaturated fatty acids are
those with only one double bond, while those with more than one double bond are
known as poly-unsaturated fatty acids or PUFA. The n-3 series and n-6 series
fatty acids, and the n-7 and n-9 fatty acids are all members of the PUFA group.
Members of this group which have many (4 or more) double bonds are sometimes
referred to as higher unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA'S).
|

